Distributed Shared Memory
Summary
- Cluster as a Parallel Machine (Sequential Program)
- Cluster as a Parallel Machine (Message Passing)
- Cluster as a Parallel Machine (Distributed Shared Memory)
- History of Shared memory Systems
- Shared Memory Programming
- Software DSM
- Non Page Based DSM
- Scalability
Cluster as a Parallel Machine (Sequential Program)
Some compilers can find parallelizable opportunities in sequential code
- High Performance Fortran allows users to explicitly define regions that can be opportunistically optimized.
- Works well for data parallel programs.
Cluster as a Parallel Machine (Message Passing)
Explicitly parallel
send/recv primitives provided, normally via library
Requires changes to how a program is conceived
Cluster as a Parallel Machine (Distributed Shared Memory)
Allow DSM library to manage memory, and allow it to be available across entire cluster
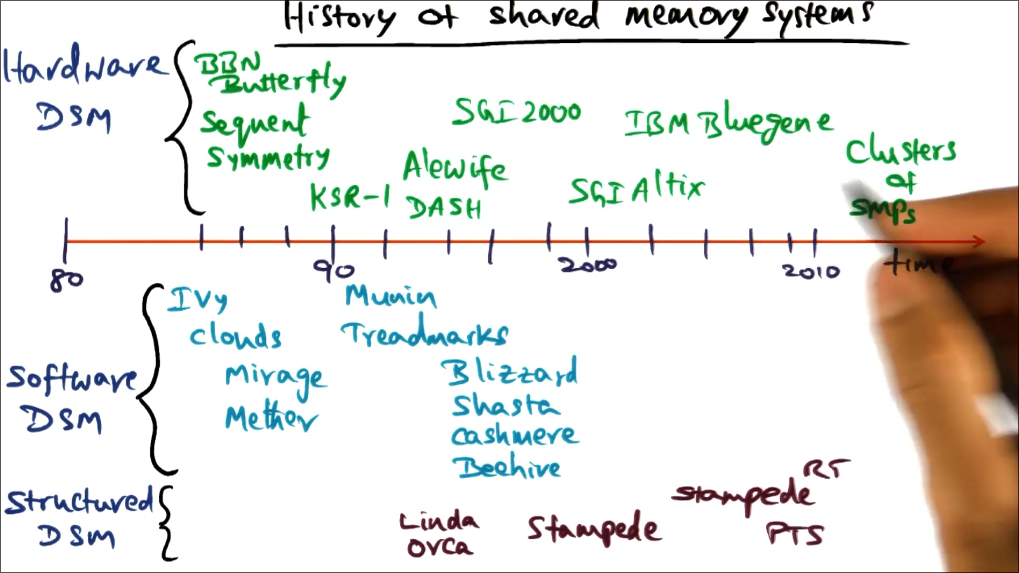
History of Shared memory Systems
Shared Memory Programming
Two types of memory access:
- normal r/w to shared data
- r/w to syncrhonization variables
Memory Consistency and Cache Coherence
Memory consistency answers, “What is the model presented to the programmer?”.
Cache coherence answers, “How is the system implementing the model in the presence of private caches?”.
Sequential Consistency
Program order + arbitrary interleaving
Does not distinguish between data r/w and synchronization r/w
Coherence action on every r/w access
lock(L);
read(a);
write(b);
unlock(L);
Worse at scaling
Release Consistency
All coherence actions prior to releasing lock, should be completed at point of release.
Distinguishes between data r/w and synchronization r/w
modify(A);
lock(L);
flag=1;
signal(c);
unlock(L);
Advantages of RC over SC
- No waiting for coherence action on every memory access
- overlap computation with communication
- better performance for RC
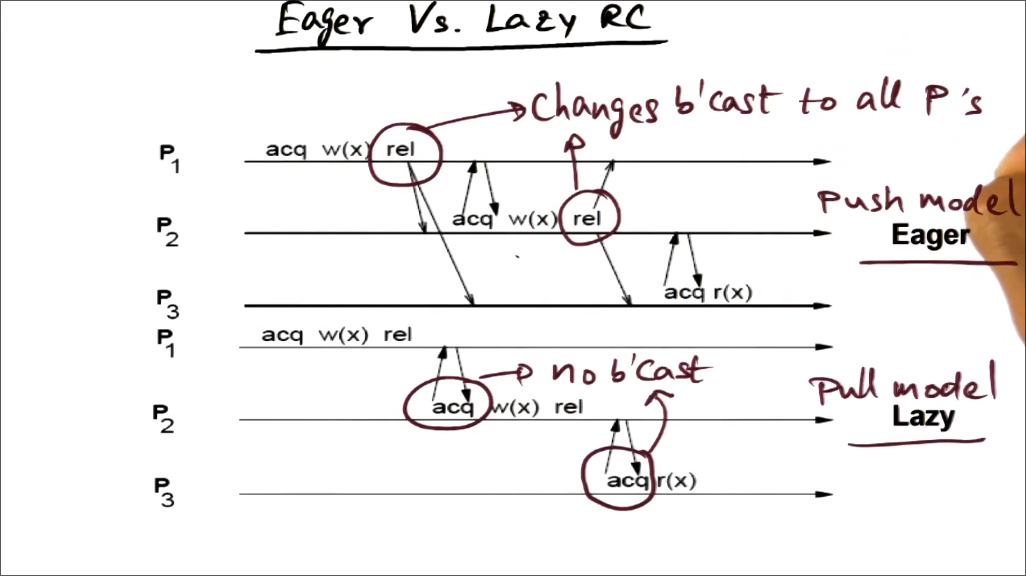
Lazy RC
All coherence actions prior to releasing lock, should be complete before acquiring the lock again.
Software DSM
Global virtual memory abstraction:
- Address space partitioned
- Address equivalence
- Distributed ownership
Coherence granularity is at page-level
- Owner of a particular page is responsible for coherence
LRC with Multi Writer Coherence Protocl
Only send page diffs
Invalidate pages at lock time
- Access to invalidated pages require page fetch
- Fetch base page and diffs
- Only fetch at point of access
Implementation
When you write to x, a copy is made. After you release x, the diff is calculated against the copy.
Diff is runlength encoded
- Basically a tuple containing start_offset and end_offset
Data races can only happen if portions of a page are under a same lock, which makes it an application problem.
If a page has more than a certain threshold of diffs, a GC loop coalesces the diffs into a new original.
Non Page Based DSM
Library-based
- Annotate shared variables
- Coherence actions inserted at point of access
Structure-based
- API for structs
- Coherence actions on API calls
Scalability
Shared memory works best when you don’t share memory.
Pointers make this worse. Yout think you’re accessing something local, but it points to a remote location which incurs implicit network calls.